Cloud computing should have reduced worldwide data center energy usage. It’s possible only if those cloud data centers are as efficient as they can be. Cloud computing and colocation data centers are friendlier than the onsite
IT infrastructure. Datacenters can supply the same IT services while consuming less energy.
According to Pike Research, cloud computing can decrease the IT carbon footprint by as much as 38%. These statistics, however, were based on the development of energy-efficient data centers. So the question is, are we delivering these energy-efficient data centers, or, have lost sight of our environmental obligations? The widespread movement of company data and IT services to the cloud has increased the demand for more eco-friendly data centers. Traditional and hyper-scale data center operators must follow the efficient design. Operating principles as corporations migrate their corporate IT infrastructures to the cloud in increasing numbers.
Typical Datacenter VS Green Datacenter?
Many of the important characteristics of a green data center are unseen. Improved heat dissipation and airflow design are examples of this. Approaches, such as free cooling, also produce superior outcomes than a typical air conditioning system. The use of containment aisles to optimize airflow has resulted in more efficient room cooling. The use of renewable energy and the discussion of water is pushing the criteria against which green data centers are assessed. To reduced usage, everything from energy storage to solar panels are being employed. The same thing goes with solutions that recycle waste energy. This energy can heat neighboring buildings, industrial establishments, and even swimming pools. Sustainable Data Center Design
Recent data states that typical data centers have reduced their energy consumption by 50% in the previous six years. Hyper-scale data centers currently consume twice as much energy as they did in 2015. Unfortunately, without the capacity to dig further into the data it’s hard to determine whether these numbers represent the rise of hyperscale data centers. This is regardless if they are less efficient than their traditional counterparts. The major driving force is the increasing demand. Though, there’s lingering hesitancy in hyper-scale data centers adopting best practices. What we do know is that, if recent efficiency gains in data center hardware and infrastructure continue. It should be able to handle a 60% growth in demand for both standard and hyper-scale data center services over the next 12 months without increasing energy consumption. However, to do this, data center operators must adhere to energy-efficient design standards.
Economic Advantage

PHOTO CREDIT: DATACENTER.HELLO.GLOBAL.NTT
Green data centers provide many environmental and cost-effective advantages. Investing in a new-generation design for a green data center might be costly at first, it would pay off in the long term. The cost of electricity and fuel necessary to power the data centers has been considerably lowered because the data centers mostly use renewable sources of energy. Furthermore, the green data center implemented methods to recycle e-waste from the data centers, resulting in a new source of money. Cool Data Centers
As showed by Fujitsu’s recent energy reductions in two of its Australian data centers. Cooling technology solutions are a critical component of energy-efficient data centers. Following the analysis of environmental data acquired by wireless sensors, a 48% decrease in energy usage was obtained by optimizing airflow and reconfiguring CRAC units. The electricity saved by Fujitsu’s efforts was comparable to 350 ordinary homes’ yearly energy usage. It is easy to see the potential for huge energy and cost reductions that cooling technology has to offer. The most interesting aspect of this specific exercise in efficiency improvements is through configuration to existing hardware. There must be no extra components required to realize the cost and energy reductions. On the cost reductions, low energy consumption resulted in a $230,000 yearly electricity savings across two data centers in Australia.
Prioritizing Toxic Waste
The potential energy savings that cooling systems may provide are appealing. However, the outlook for hazardous waste is less promising. In the United States, e-waste accounts for 70% of all hazardous trash. There’s no reason to assume the numbers are much better elsewhere in the industrialized world. Supermicro conducted a survey of more than 5,000 data center specialists last 2019. The number of enterprises working with authorized recycling services had fallen by 14% year over year. This is while the number of businesses recycling their own hardware had decreased by 5%. These are not industry trends to be proud of. The potential for improvement in this area must be prioritized. Datacenter operators may reduce worldwide e-waste by as much as 80% by improving hardware refresh cycles, according to the same study. 
PHOTO CREDIT: WIRED.COM
Can Data Centers be Made Carbon Neutral?
Online accessibility has completely become part of our daily lives. The pandemic has accelerated the move to a digital lifestyle. From working from home, homeschooling, connecting with loved ones, and relaxing. And this set-up seems to be staying for the foreseeable future. Our digital lifestyle has resulted in increased Internet traffic. Which resulted in an increase in the demand for the data centers. The video calls, streaming services, and various messaging apps are used on a work-from-home setup. It’s no surprise that each individual produced 1.7MB of data per second in 2020. That summarizes how 90% of the world’s data was only generated from the last two years.
Conversion to a Green Data Center
The construction of a GDC is a large investment. Several steps need to be taken when a government or business entity considers the conversion of an existing data center to a GDC. The first and the foremost step is the evaluation of your data center in terms of energy efficiency. This step includes monitoring and measuring the consumption of energy for the entire enterprise. This initial step of monitoring the energy consumption allows the enterprise to estimate where energy consumption can be reduced. This activity obviously helps in the consideration to redesign or start a new data center.
There are metrics that can help in analyzing the “greenness” of an existing data center. Two of the most popular metrics that can measure the “greenness” of an existing data center are:
These metrics are calculated based on the following equations:

PHOTO CREDIT: WWW.WEBWIZ.NET

PHOTO CREDIT: FUTURECDN.NET
AKCPro Server – Live PUE Calculations
AKCPro Server is an ideal DCIM solution. Perfect for those people who don’t have the budget or need for complex DCIM software, but require a capable monitoring system for their data center. With many advanced features such as Cabinet Thermal Mapping, Drill Down Mapping, Graphing, VPN connections to remote sites, AKCPro Server is the ideal choice. AKCPro Server is capable of live PUE calculations, so you can see real-time the effect changes you make have on your PUE.
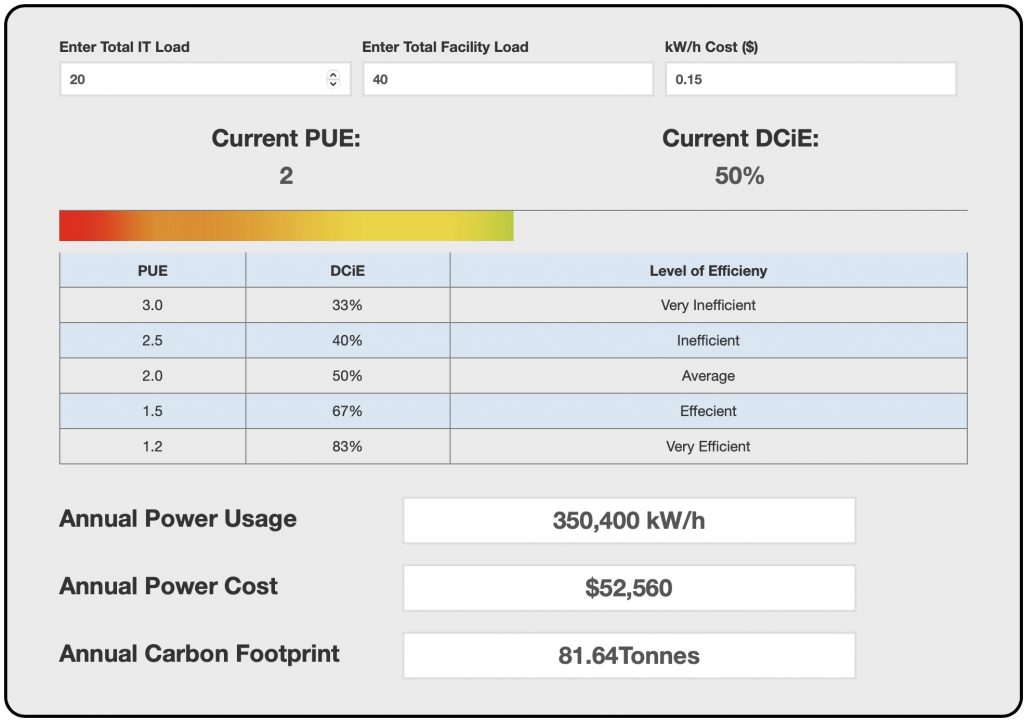
AKCP PUE CALCULATOR
By utilizing the AKCPro Server live PUE calculations you can see the immediate effect that changing your power usage has. Shut down fans and cooling systems and see how it improves your PUE. At the same time, use thermal rack maps to ensure that you are not overheating any servers. Adjusting the thermostat on your CRAC units will undoubtedly result in improved PUE, but what about its knock-on effect on the lifespan of servers?
By employing the complete AKCP ecosystem of products, Thermal Map Sensors, AKCPro Server and Power Meters work together to give a complete analysis and assistance in cutting your power costs and improving your PUE.
Moving Forward
Creating green data centers that provide tangible benefits for the environment. A rigorous, holistic approach has to be laid for the design and operation of data centers. This has to address cooling, energy consumption, and waste. Listed below are the factors that need to be considered as cloud migration become more commonplace:
Servers with Low Power Consumption — Installing servers with low power consumption in mind.
More Efficient Cooling Solutions — Reconfiguring current systems based on environmental data analysis.
- Implementing AKCP Monitoring System — Monitors power usage and the ecosystem of the whole data center.
Optimized Hardware Refresh Cycles — Reducing hazardous waste via life cycle assessment and refresh cycle optimization of all data center hardware components.
These key areas should be focused on to achieve the predicted reduction in the carbon footprint of the global IT industry that clouds computing has made possible.
Reference Links:
https://nsidc.org/about/green-data-center
https://www.silvertouch.com/blog/how-green-data-center-benefits-modern-business-and-environment/https://nsidc.org/about/green-data-center
https://modius.com/green-data-center-initiatives/
https://www.aabri.com/manuscripts/10516.pdf






Big Data is a collection of large and complex data sets that contains structured and unstructured data which may be difficult to process and analyze using traditional database management tools. www.inetsoft.com
ReplyDelete